The cloud has transformed the way businesses operate, offering unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. However, the world of cloud computing can be complex, with various deployment models to choose from. Understanding these models is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about their IT infrastructure. Let’s explore the main types of cloud deployment models available and their implications for businesses.
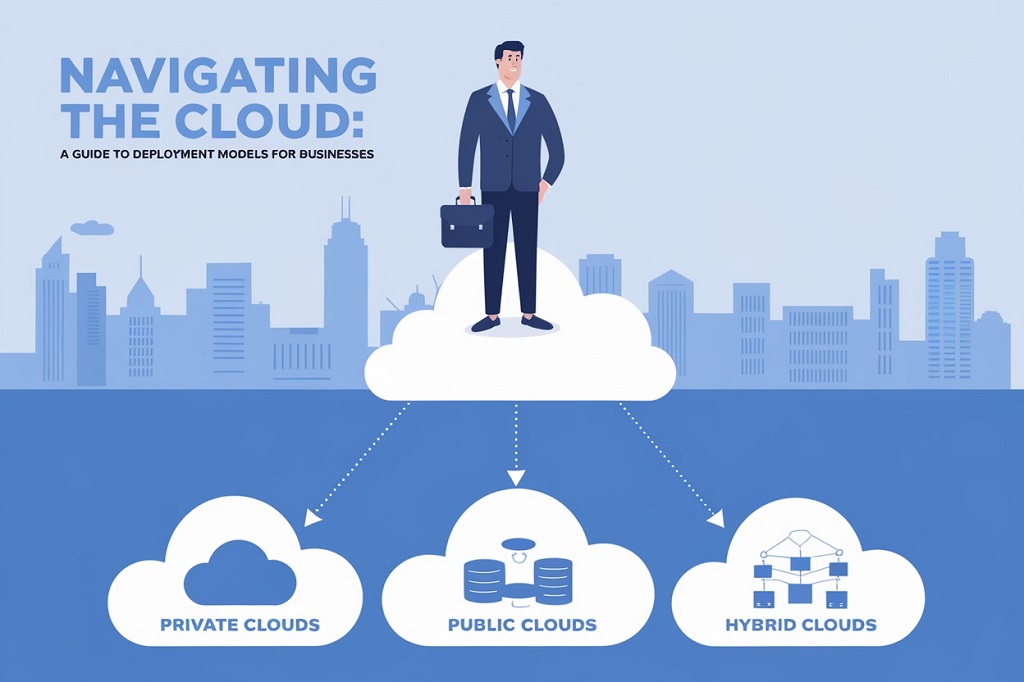
Public Cloud
The public cloud is the most common and widely recognized deployment model. In this model, cloud resources (servers, storage, databases, etc.) are owned and operated by a third-party cloud provider (such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform) and shared among multiple tenants. Businesses access these resources over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Advantages:
Cost-Efficiency: No upfront capital investment is required; businesses only pay for what they use.
Scalability: Resources can be easily scaled up or down based on demand.
Reliability: Cloud providers typically have robust infrastructure with high availability.
Accessibility: Resources can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
Read More Also: Why is It Important to Learn About Cybersecurity?
Disadvantages:
Security Concerns: Data security and privacy can be a concern as resources are shared with other tenants.
Limited Control: Businesses have limited control over the underlying infrastructure.
Compliance Issues: Some industries have strict compliance requirements that may be difficult to meet in a public cloud environment.
Ideal for:
Startups and small businesses with limited budgets.
Businesses with fluctuating workloads.
Applications that require high availability and scalability.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a dedicated cloud environment that is exclusively used by a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or off-premises by a third-party provider.
Advantages:
Enhanced Security and Control: Businesses have complete control over their data and infrastructure, offering increased security and privacy.
Customization: The private cloud can be tailored to the specific needs and requirements of the business.
Compliance: Easier to meet industry-specific compliance regulations.
Disadvantages:
Higher Costs: Upfront capital investment and ongoing maintenance costs can be significant.
Limited Scalability: Scaling resources can be more challenging and time-consuming compared to the public cloud.
Management Complexity: Requires specialized IT expertise to manage and maintain the private cloud.
Ideal for:
Large enterprises with sensitive data or strict compliance requirements.
Businesses that require a high degree of control over their IT infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing businesses to leverage the benefits of each model. Workloads can be strategically placed in either the public or private cloud based on factors such as security, cost, and performance requirements.
Advantages:
Flexibility: Businesses have the flexibility to choose the best cloud environment for each workload.
Cost Optimization: Less sensitive data can be stored in the cost-effective public cloud while sensitive data remains in the secure private cloud.
Scalability: The public cloud can be used for burst workloads or temporary capacity needs.
Business Continuity: Critical applications can be replicated across both clouds for disaster recovery.
Disadvantages:
Complexity: Managing and integrating multiple cloud environments can be complex.
Network Latency: Data transfer between public and private clouds can introduce latency.
Security Challenges: Ensuring consistent security policies across both clouds can be challenging.
Ideal for:
Businesses that want the flexibility to move workloads between public and private clouds.
Organizations with varying data sensitivity and compliance requirements.
Multi-Cloud
A multi-cloud strategy involves using multiple cloud providers (public or private) to avoid vendor lock-in and take advantage of the unique strengths of each provider.
Advantages:
Vendor Independence: Reduces reliance on a single cloud provider.
Best-of-Breed Solutions: Businesses can choose the best cloud services from different providers.
Cost Optimization: Increased bargaining power and the ability to take advantage of competitive pricing.
Resilience: Minimizes the risk of service disruptions by diversifying cloud providers.
Disadvantages:
Complexity: Managing multiple cloud environments can be even more complex than a hybrid cloud.
Integration Challenges: Integrating services from different providers can be difficult.
Skillset Requirements: IT teams need expertise in managing multiple cloud platforms.
Ideal for:
Large enterprises with complex IT requirements.
Businesses that want to avoid vendor lock-in and leverage the strengths of different cloud providers.
Choosing the Right Deployment Model
Selecting the right cloud deployment model is a critical decision that depends on several factors, including:
Business Needs: Consider the specific requirements of your business, such as data sensitivity, compliance, scalability, and budget.
Workload Characteristics: Analyze the characteristics of your workloads, including security, performance, and availability requirements.
IT Expertise: Evaluate your in-house IT capabilities and the resources available to manage different cloud environments.
Conclusion:
Cloud deployment models offer businesses a range of options to meet their IT needs. The public cloud provides cost-efficiency and scalability, while the private cloud offers enhanced security and control. The hybrid cloud combines the benefits of both models, and the multi-cloud strategy offers vendor independence and flexibility.
By carefully considering your business requirements and workload characteristics, you can choose the cloud deployment model that best aligns with your goals and sets your business up for success in the digital age. Remember, the cloud is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and the right model for your business will depend on your unique circumstances and priorities.